

Alternatively, a vacant lot in a flat suburban neighborhood would have a low cost in these three respects, but the land may be more expensive to purchase.
For example, if one is planning a paved bicycling path, a location on a steep wooded slope would likely mean high construction costs, high negative impacts to the natural environment, and higher energy costs for riders trying to bicycle up the slope.

Negative impacts to the human environment (e.g., destroying homes or historic structures)Ĭonceptually, one could "measure" the cost of a path crossing any unit area of space.Negative impacts to the natural environment (e.g., crossing wetlands or clearing forests).Travel energy expenditure (e.g., vehicle fuel usage).Depending on the particular application, these could include:

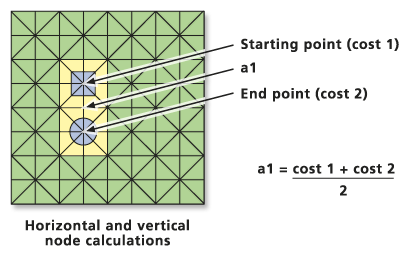
Although actual financial expenses can be part of it, the notion of "cost" is typically used for any negative impact of moving over a space. This cost can be measured in any number of ways. If one wants to minimize this energy expenditure cost, then it may be better to walk around a body of water than swim straight through it, even though the actual distance is greater. For example, if the cost of a person traveling over any space is measured as the amount of energy expended, then moving over water (i.e., swimming) has a far greater cost than moving over land (i.e., walking). Cost distance employs the geographic principle of Friction of Distance, which states that there is a cost or impedance associated with moving a unit distance over any location, and this cost varies over space (and can thus be conceptualized as a field). There are many ways to measure the distance between two points that are relevant to GIS, including Euclidean distance (an unconstrained straight line), Geodesic distance (when travel is constrained to the surface of a sphere), and network distance (when travel is constrained to a linear network). These tools are most useful in applications for planning new routes for constructing linear infrastructure, like roads or utilities, or for modeling movements across the landscape that do not follow established routes, such as wildlife migration.Ĭost distance is "the notion of an alternative family of distance metrics". Cost Distance Analysis, on the other hand, evaluates costs over continuous space. Network Analysis is also based on the notion of finding routes that minimize costs, but restrict the possible routes to a preexisting network.
Cost of arcgis software#
Most GIS software consists of several algorithms and tools for performing different kinds of cost distance analysis. Although the notion of cost-based proximity analysis dates back to the 1950s, GIS has made such studies practical. Cost distance analysis, also known as Accumulated Cost Surface Analysis, is the analysis of movement over continuous space, in which the cost of moving through any location is variable, so that some paths of movement have higher costs than others. This map shows the results of a spatial model to calculate the least cost path between a stand of forest being cut and the nearest sawmill.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
